해당 내용은 Udemy의 Certified Kubernetes Administrator (CKA) with Practice Tests 강의를 공부한 내용입니다. 내용을 그대로 번역하기보다는, 제가 이해하기 쉬운 대로 수정한 부분들이 있습니다.
⚠️ 영어 독해가 많이 부족합니다. 틀린 내용이 있으면 알려주시면 감사하겠습니다.
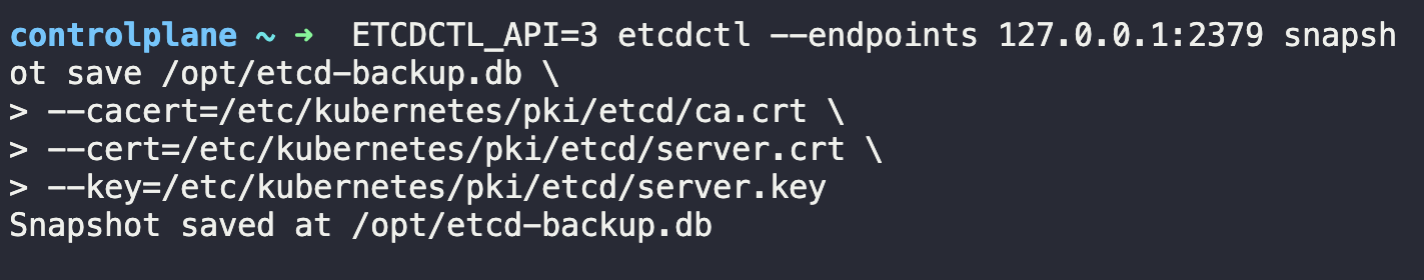
1. Take a backup of the etcd cluster and save it to /opt/etcd-backup.db.
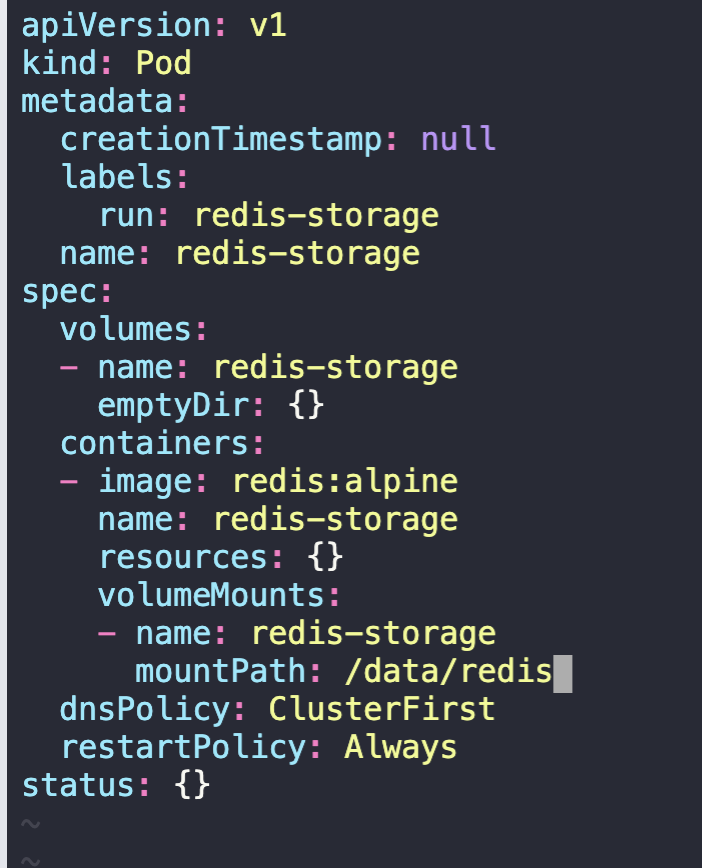
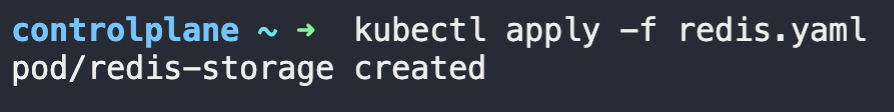
2. Create a Pod called redis-storage with image: redis:alpine with a Volume of type emptyDir that lasts for the life of the Pod.
-
Pod named 'redis-storage' created
-
Pod 'redis-storage' uses Volume type of emptyDir
- Pod 'redis-storage' uses volumeMount with mountPath = /data/redis

3. Create a new pod called super-user-pod with image busybox:1.28. Allow the pod to be able to set system_time.
The container should sleep for 4800 seconds.
-
Pod: super-user-pod
-
Container Image: busybox:1.28
-
SYS_TIME capabilities for the conatiner?

apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
creationTimestamp: null
name: super-user-pod
spec:
containers:
- image: busybox:1.28
name: super-user-pod
command: ["sleep", "4800"]
securityContext:
capabilities:
add: ["SYS_TIME"]4. A pod definition file is created at /root/CKA/use-pv.yaml. Make use of this manifest file and mount the persistent volume called pv-1. Ensure the pod is running and the PV is bound.
mountPath: /data
persistentVolumeClaim Name: my-pvc
-
persistentVolume Claim configured correctly
-
pod using the correct mountPath
-
pod using the persistent volume claim?
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: my-pvc
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 10MiapiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
creationTimestamp: null
labels:
run: use-pv
name: use-pv
spec:
containers:
- image: nginx
name: use-pv
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: "/data"
name: mypod
volumes:
- name: mypod
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: my-pvc5. Create a new deployment called nginx-deploy, with image nginx:1.16 and 1 replica. Next upgrade the deployment to version 1.17 using rolling update.
-
Deployment : nginx-deploy. Image: nginx:1.16
-
Image: nginx:1.16
-
Task: Upgrade the version of the deployment to 1:17
-
Task: Record the changes for the image upgrade
For Kubernetes Version <=1.17
kubectl run nginx-deploy --image=nginx:1.16 --replicas=1 --record
kubectl rollout history deployment nginx-deploy
kubectl set image deployment/nginx-deploy nginx=nginx:1.17 --record
kubectl rollout history deployment nginx-deployFor Kubernetes Version >1.17
kubectl create deployment nginx-deploy --image=nginx:1.16 --dry-run=client -o yaml > deploy.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-deploy
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx-deploy
strategy: {}
template:
metadata:
creationTimestamp: null
labels:
app: nginx-deploy
spec:
containers:
- image: nginx:1.16
name: nginxkubectl create -f deploy.yaml --record
kubectl rollout history deployment nginx-deploy
kubectl set image deployment/nginx-deploy nginx=nginx:1.17 --record
kubectl rollout history deployment nginx-deploy6. Create a new user called john. Grant him access to the cluster. John should have permission to create, list, get, update and delete pods in the development namespace . The private key exists in the location: /root/CKA/john.key and csr at /root/CKA/john.csr.
Important Note: As of kubernetes 1.19, the CertificateSigningRequest object expects a signerName.
Please refer the documentation to see an example. The documentation tab is available at the top right of terminal.
-
CSR: john-developer Status:Approved
-
Role Name: developer, namespace: development, Resource: Pods
-
Access: User 'john' has appropriate permissions
apiVersion: certificates.k8s.io/v1
kind: CertificateSigningRequest
metadata:
name: john-developer
spec:
signerName: kubernetes.io/kube-apiserver-client
request: LS0tLS1CRUdJTiBDRVJUSUZJQ0FURSBSRVFVRVNULS0tLS0KTUlJQ1ZEQ0NBVHdDQVFBd0R6RU5NQXNHQTFVRUF3d0VhbTlvYmpDQ0FTSXdEUVlKS29aSWh2Y05BUUVCQlFBRApnZ0VQQURDQ0FRb0NnZ0VCQUt2Um1tQ0h2ZjBrTHNldlF3aWVKSzcrVVdRck04ZGtkdzkyYUJTdG1uUVNhMGFPCjV3c3cwbVZyNkNjcEJFRmVreHk5NUVydkgyTHhqQTNiSHVsTVVub2ZkUU9rbjYra1NNY2o3TzdWYlBld2k2OEIKa3JoM2prRFNuZGFvV1NPWXBKOFg1WUZ5c2ZvNUpxby82YU92czFGcEc3bm5SMG1JYWpySTlNVVFEdTVncGw4bgpjakY0TG4vQ3NEb3o3QXNadEgwcVpwc0dXYVpURTBKOWNrQmswZWhiV2tMeDJUK3pEYzlmaDVIMjZsSE4zbHM4CktiSlRuSnY3WDFsNndCeTN5WUFUSXRNclpUR28wZ2c1QS9uREZ4SXdHcXNlMTdLZDRaa1k3RDJIZ3R4UytkMEMKMTNBeHNVdzQyWVZ6ZzhkYXJzVGRMZzcxQ2NaanRxdS9YSmlyQmxVQ0F3RUFBYUFBTUEwR0NTcUdTSWIzRFFFQgpDd1VBQTRJQkFRQ1VKTnNMelBKczB2czlGTTVpUzJ0akMyaVYvdXptcmwxTGNUTStsbXpSODNsS09uL0NoMTZlClNLNHplRlFtbGF0c0hCOGZBU2ZhQnRaOUJ2UnVlMUZnbHk1b2VuTk5LaW9FMnc3TUx1a0oyODBWRWFxUjN2SSsKNzRiNnduNkhYclJsYVhaM25VMTFQVTlsT3RBSGxQeDNYVWpCVk5QaGhlUlBmR3p3TTRselZuQW5mNm96bEtxSgpvT3RORStlZ2FYWDdvc3BvZmdWZWVqc25Yd0RjZ05pSFFTbDgzSkljUCtjOVBHMDJtNyt0NmpJU3VoRllTVjZtCmlqblNucHBKZWhFUGxPMkFNcmJzU0VpaFB1N294Wm9iZDFtdWF4bWtVa0NoSzZLeGV0RjVEdWhRMi80NEMvSDIKOWk1bnpMMlRST3RndGRJZjAveUF5N05COHlOY3FPR0QKLS0tLS1FTkQgQ0VSVElGSUNBVEUgUkVRVUVTVC0tLS0tCg==
usages:
- digital signature
- key encipherment
- client auth
groups:
- system:authenticatedkubectl certificate approve john-developer
kubectl create role developer --resource=pods --verb=create,list,get,update,delete --namespace=development
kubectl create rolebinding developer-role-binding --role=developer --user=john --namespace=development
kubectl auth can-i update pods --as=john --namespace=development7. Create a nginx pod called nginx-resolver using image nginx, expose it internally with a service called nginx-resolver-service. Test that you are able to look up the service and pod names from within the cluster. Use the image: busybox:1.28 for dns lookup. Record results in /root/CKA/nginx.svc and /root/CKA/nginx.pod
-
Pod: nginx-resolver created
-
Service DNS Resolution recorded correctly
- Pod DNS resolution recorded correctly
kubectl run nginx-resolver --image=nginx
kubectl expose pod nginx-resolver --name=nginx-resolver-service --port=80 --target-port=80 --type=ClusterIP
kubectl run test-nslookup --image=busybox:1.28 --rm -it --restart=Never -- nslookup nginx-resolver-service
kubectl run test-nslookup --image=busybox:1.28 --rm -it --restart=Never -- nslookup nginx-resolver-service > /root/CKA/nginx.svc
Get the IP of the nginx-resolver pod and replace the dots(.) with hyphon(-) which will be used below.
kubectl get pod nginx-resolver -o wide
kubectl run test-nslookup --image=busybox:1.28 --rm -it --restart=Never -- nslookup <P-O-D-I-P.default.pod> > /root/CKA/nginx.pod8. Create a static pod on node01 called nginx-critical with image nginx and make sure that it is recreated/restarted automatically in case of a failure.
Use /etc/kubernetes/manifests as the Static Pod path for example.
-
static pod configured under /etc/kubernetes/manifests ?
-
Pod nginx-critical-node01 is up and running
kubectl run nginx-critical --image=nginx --dry-run=client -o yaml > static.yaml
cat static.yaml - Copy the contents of this file.
kubectl get nodes -o wide
ssh node01
OR
ssh <IP of node01>
Check if static-pod directory is present which is /etc/kubernetes/manifests if not then create it.
mkdir -p /etc/kubernetes/manifests
Paste the contents of the file(static.yaml) copied in the first step to file nginx-critical.yaml.
Move/copy the nginx-critical.yaml to path /etc/kubernetes/manifests/
cp nginx-critical.yaml /etc/kubernetes/manifests
Go back to master node
kubectl get pods'MLOps > Doker & Kubernetes' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Udemy CKA 강의 정리 77: Practice Test - Multiple Schedulers (0) | 2023.02.21 |
|---|---|
| Udemy CKA 강의 정리 76: Multiple Schedulers (0) | 2023.02.21 |
| Udemy CKA 강의 정리 267: Mock Exam -2 (0) | 2023.02.02 |
| Udemy CKA 강의 정리 257: Network Troubleshooting (0) | 2023.02.01 |
| Udemy CKA 강의 정리 254: Worker Node Failure (0) | 2023.02.01 |

댓글